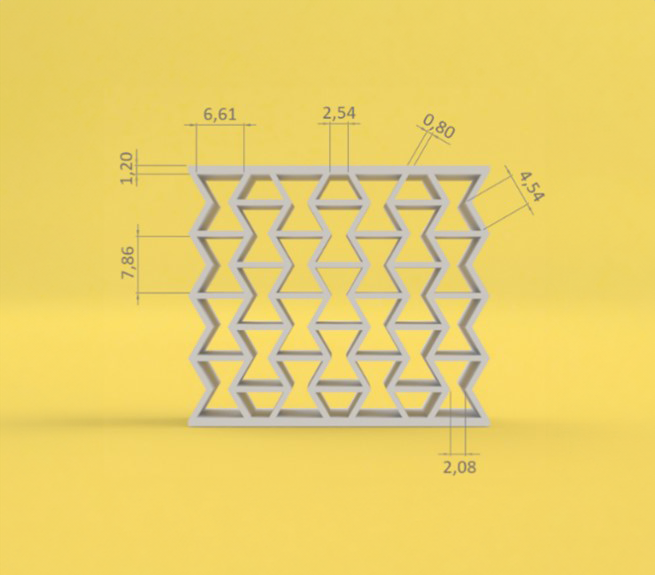
The research “4D Printing of PLA/PBS Biopolymers: Impact of Polymer Grade Variations on Thermomechanical Performance” specifically focuses on blends of PLA and PBS, with 80% PLA combined with 20% PBS. This composition leverages the strengths of both materials: PLA provides high mechanical strength and shape memory properties, while PBS offers flexibility and toughness. By varying PBS grades (FZ71 and FZ91), the study investigates how these choices optimize energy absorption, mechanical properties, and shape recovery of 4D-printed structures.
Polymer Grade Variations: The Key to Optimized Performance
The results show that polymer grade variations play a crucial role. For example, a higher melt flow index (PBS FZ71) leads to more flexibility and energy absorption, while a higher molecular weight (PBS FZ91) results in better structural integrity and a higher shape recovery rate. This enables the development of structures that can adapt to specific applications in sectors such as construction, aerospace, and other high-tech industries.
This research not only contributes to the sustainability of materials but also opens up new possibilities for 4D printing technology. With the right material choices, smart, shape-changing structures can be optimized for a wide range of applications.